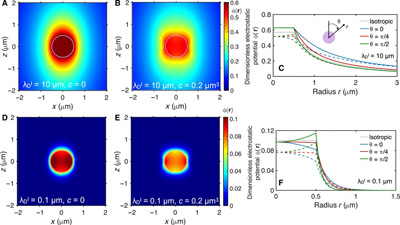
The physical behavior of anisotropic charged colloidal particles in nematic solvents is determined by their dielectric anisotropy. Together with the experimental group of Professor Ivan Smalyukh at University of Colorado Boulder the authors Jeffrey C. Everts and Miha Ravnik from the Faculty of Mathematics and Physics at University of Ljubljana and the Department F5 of Jozef Stefan Institute demonstrated anisotropic electrostatic screening for charged colloidal particles in nematic electrolytes. The electrostatic potential and pair interactions decay with an anisotropic Debye screening length, contrasting constant screening length for isotropic electrolytes. Charged dumpling-shaped near-spherical colloidal particles in nematic media are used as model systems, demonstrating competing anisotropic elastic and electrostatic effective pair interactions for colloidal surface charges tunable from neutral to high, yielding particle-separated metastable states (Science Advances 2021, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abd0662). The work was published in Science Advances and contributes to the understanding of electrostatic screening in nematic media.